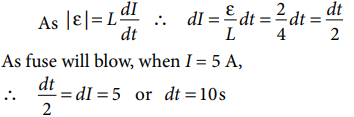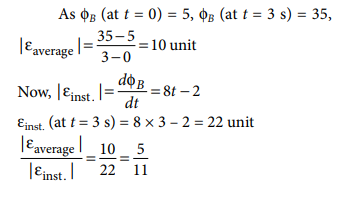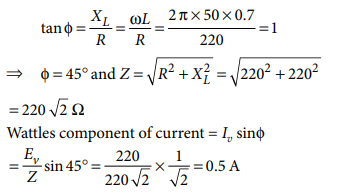Many important questions are formed in competitive exams like CUET, JEE, NEET, and boards from Class 12 Physics Unit 4. Below, we have provided Important Questions from Class 12 Physics Unit 4 Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents for your JEE Mains 2023 preparation. You can check it here for revision purposes.
Latest: JEE Main Physics Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents Class 12 JEE Mains Questions and Answers
We’ve compiled a list of important questions about the Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents physics class 12 unit 4 that you should not miss while studying for your JEE Main Exams.
Q.1. In the circuit shown in figure, the cell is ideal. The coil has an inductance of 4 H and zero resistance. F is fuse of zero resistance and will blow when the current through it reaches 5 A. The switch is closed at t = 0. The fuse will blow
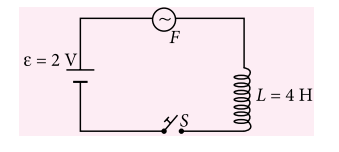
(a) almost at once
(b) after 2 s
(c) after 5 s
(d) after 10 s
A.1. (d)
Explanation:
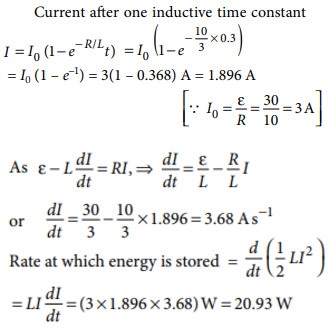
Q.2. A 3 H inductor is placed in series with a 10 W resistor. An emf of 30 V is being applied suddenly to the combination. At 0.3 s (which is one inductive time constant) after start, find at which rate energy is stored in the inductor.
(a) 20.93 W (b) 2.083 W
(c) 209.3 W (d) 31.83 W
A.2. (a)
Explanation:
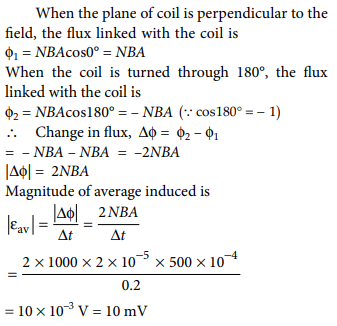
Q.3. A coil has 1000 turns and 500 cm2 as its area. The plane of the coil is placed perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 2 × 10–5 T. The coil is rotated through 180° in 0.2 s. The average emf induced in the coil, in mV is
(a) 5 (b) 10 (c) 15 (d) 20
A.3. (b)
Explanation:
Q.4. What is the value of inductance L for which the current is maximum in a series LCR circuit with C = 10 µF and ω = 1000 s–1 ?
(a) 100 mH
(b) 1 mH
(c) 10 mH
(d) can not be calculated unless R is known
A.4. (a)
Q.5. A 150 Ω resistor and an inductance L are connected in series to a 200 V, 50 Hz source of negligible impedance. The current comes to 1 A. When the source is changed to 400 V, 100 Hz, the current will be
(a) less than 1 A
(b) 1 A
(c) between 1 A and 2 A
(d) between 2 A and 4 A
A.5. (c)
Q.6. The flux linked with a coil is given by ΦB = 4t2– 2t + 5. The ratio of the average emf between 0 to 3 s and instantaneous emf at 3 s is
(a) 1 (b) 5/11 (c) 11/5 (d) 11
A.6. (b)
Explanation:
Q.7. A coil has an inductance of 0.7 H and is joined in series with a resistance of 220 Ω. When an alternative emf. of 220 V at 50 cps is applied to it, then the wattles component of the current in the circuit is
(a) 5 A (b) 0.5 A (c) 0.7 A (d) 7 A
A.7. (b)
Explanation:
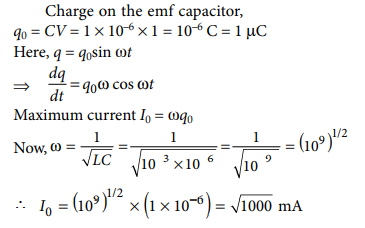
Q.8. A capacitor of capacitance 1 μF is charged to a potential of 1 V. It is connected in parallel to an inductor of inductance 10–3 H. The maximum current that will flow in the circuit has the value
(a) √1000 m A (b) 1 m A
(c) 10 m A (d) 1000 m A
A.8. (a)
Explanation:
Q.9. Find the value of the phase difference between the current and the voltage in the series LCR circuit shown below.
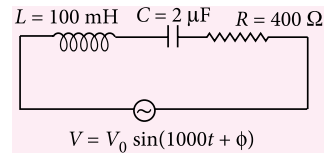
(a) 30° (b) 45° (c) 60° (d) 50°
A.9. (b)
Q.10. A variable voltage V = 2t is applied across an inductor of inductance L = 2 H as shown in figure. Then choose wrong option.
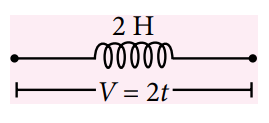
(a) Current versus time graph is a parabola.
(b) Energy stored in magnetic field at t = 2 s is 4 J.
(c) Potential energy at time t = 1 s in magnetic field is increasing at a rate of 1 J s–1.
(d) Energy stored in magnetic field is zero all the time.
A.10. (d)
Explanation:
All the best