Many important questions are formed in competitive exams like NEET and boards from Class 11 Biology Chapter 14. Respiration in Plants is the fourteenth chapter in the Class 11 NEET syllabus for Biology. Below, we have provided Important Questions from Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants for your NEET 2023 preparation. You can check it here for revision purposes.
Latest: Mineral Nutrition NEET Questions and Answers
Respiration in Plants Class 11 NEET Questions and Answers
We’ve compiled a list of essential questions about the Respiration in Plants biology class 11 chapter 14 that you should not miss while studying for your NEET Exams.
Respiration in Plants MCQ for NEET
How much amount of energy will be liberated from 2 mole of glucose through cellular respiration?
In the given experiment, test tube containing potassium hydroxide is suspended so that

Which of the following steps is associated with NADH formation during TCA cycle?
If both fatty acids and carbohydrates are available to muscles, which will be consumed first during respiration?
Consider the following statements and select the correct option. (i) Acetaldehyde is reduced to ethyl alcohol or ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase in yeasts during anaerobic condition. (ii) A molecule of GTP is synthesised during the conversion of succinic acid to succinyl CoA. (iii) Enzyme fumarase helps to convert fumarate into malate by addition of one molecule of water. (iv) Fermentation generally utilises NADH produced during glycolysis.
Which of the following enzymes participate in fermentation?
How many protons passes through F0 from the intermembrane space to matrix for synthesis of one ATP molecule during electron transport chain?
Respiration in Plants Match the Following Questions for NEET
Match column I with column II.
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| A. Lactic acid | (i) Respiratory quotient |
| B. Respirometer | (ii) Oxidative decarboxylation |
| C. Pyruvate dehydrogenase | (iii) Muscle fatigue |
| D. Cytochromes | (iv) Isomerisation |
| E. Phosphoglycero- mutase | (v) Inner mitochondrial |
A. A-(iii); B-(i); C-(ii); D-(v); E-(iv)
Respiration in Plants Assertion and Reason Questions for NEET
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given and a corresponding statement of Reason (R) is given just below it. Of the statements, pick the correct answer as :
Assertion : Yeast produces ethyl alcohol during anaerobic respiration. Reason : Accumulation of alcohol, produced by fermentation, beyond a certain limit can kill the microorganism.
Assertion : About 50% of the energy liberated during cellular respiration is used for synthesis of biomolecules and other life activities. Reason : Energy is liberated in controlled fashion in several steps and is mostly stored in ATP
Assertion : An intermediate RQ value is obtained where an organism is undergoing both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Reason : RQ values indicate that living organisms always use a single respiratory substrate.
Assertion : 3-phosphoglycerate is changed to 2-phosphoglycerate by isomerisation during glycolysis. Reason : Isomerisation of 3-phosphoglycerate is an energy spending phase of glycolysis.
Assertion : An electron gradient formed on the inner mitochondrial membrane forms ATP. Reason : F1 particles are present in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Assertion : The passage of electrons in electron transport chain is a downhill journey. Reason : Electron passes from one enzyme to the next with a loss of energy at each step.
Assertion : Substrate level phosphorylation is not present in Krebs' cycle. Reason : Substrate level phosphorylation involves direct synthesis of ATP from metabolites.
Assertion : Oxidative phosphorylation is linked to terminal oxidation of reduced coenzymes NADH and FADH2 in respiration. Reason : The coenzymes release electrons that pass over a series of carriers in electron transport chain
Assertion : Fats are used as respiratory substrates by a number of organisms. Reason : Fats contain more energy as compared to carbohydrates.
Assertion : Glycolysis uses oxygen as terminal oxidant. Reason : Glycolysis involves partial oxidation of glucose to pyruvic acid.
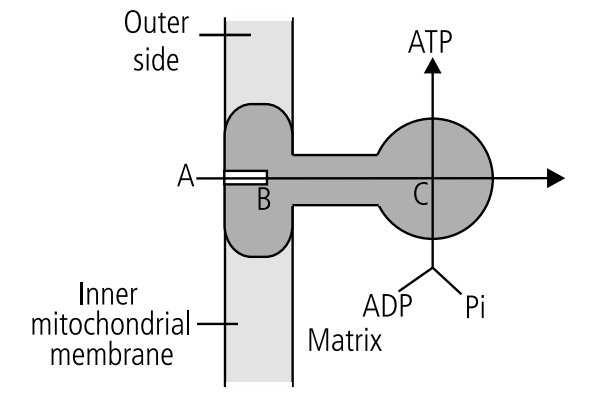
Respiration in Plants Figure-Based Questions for NEET
Study the given figure and answer the following questions.
(a) Identify A, B and C in the given figure.
A. The given figure is showing ATP synthesis by F0 – F1 particle. Here, A is 2H+, B is F0 and C is F1.
(b) How does a proton gradient develop in the system?
A. F0 – F1 particles are present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. ATP synthase becomes active when there is a proton gradient having higher concentration of H+ on the F0 side as compared to F1 side. Increased proton concentration in outer surface of inner mitochondrial membrane is produced by the pushing of protons with the help of energy liberated by passage of electrons from one carrier to another during electron transport chain.
(c) At which condition will C produce ATP?
A. The flow of protons through the F0 channel induces F1 particle to function as ATP synthase. The energy of the proton gradient is used in attaching a phosphate radicle to ADP by high energy bond and this helps in producing ATP.
Preparing for NEET? Don’t forget to check Chapterwise Important Questions–
- The Living World NEET Questions and Answers
- Biological Classification NEET Questions and Answers
- Plant Kingdom NEET Questions and Answers
- Animal Kingdom NEET Questions and Answers
- Electrostatics NEET Questions and Answers
- Morphology of Flowering Plants NEET Questions and Answers
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants NEET Questions and Answers
- Structural Organisation in Animals NEET Questions and Answers
- Cell the Unit of Life NEET Questions and Answers
- Biomolecules NEET Questions and Answers
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division NEET Questions and Answers
- Transport in Plants NEET Questions and Answers
Best & Most Recommended Books for NEET UG 2023 Exam
|
NEET Champion
|
35 Years NEET Chapter-wise Solutions
|