
Mathematical equations provide unique perspectives on the world and help us make sense of reality and see things we hadn’t noticed before. It’s no surprise that advances in math have frequently coincided with advances in our understanding of the universe. This planet has produced brilliant mathematicians and physicists in the past. Their discoveries have made our lives easier by providing us with elements such as electricity, which we cannot live without today. Thus, today we talk about the tremendous math discoveries that changed the world.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Rudolf Clausius proposed this law in 1850.
- It asserts that energy always flows from high to low concentration.
- Furthermore, it becomes less useful when energy transfers or moves because it loses energy along the way.
- This discovery paved the way for later inventions such as electricity and combustion engines.
You will also like: 10 Cool Math Tricks To Amaze Your Friends
Pythagorean Theorem
- Hippasus of Metapontum discovered that an isosceles right triangle with two base sides of one-unit length has a hypotenuse, the square root of 2, which is an irrational number.
- Along with being helpful in construction, navigation, mapmaking, and other vital processes, the Pythagorean theorem contributed to expanding the concept of numbers.
- Pythagoras’ theorem states that the sum of the squares of two sides of a right triangle equals the square of the hypotenuse.
Check Out:Top Scientific Discoveries of 2022
Law of Gravity
- You’ve probably heard the story: Isaac Newton was sitting under an apple tree one day when one apple fell and hit him on the head. Newton discovered gravity as a result of a fortunate event.
- It states that force equals an object’s mass multiplied by its acceleration, where the Equation is F = ma.
- Further, this law, combined with Newton’s other observations, led him to describe what is now known as Newton’s law of universal gravitation in 1687. F = G (m1 * m2) / r2, where m1 and m2 are the masses of two objects, and r is the distance between them.
- Since then, these ideas have been applied to many physical systems, including the motion of planets in the solar system and the use of rockets to travel between them.
 Maxwell’s Equation
Maxwell’s Equation
- It is a collection of four equations derived by mathematician James Clerk Maxwell that depict the relationship between electricity and magnetism.
- Maxwell’s equations are closely related to relativity theory.
- These equations have numerous applications, but let’s say we use them to build computers, start MRI machines in hospitals, and generate electricity.
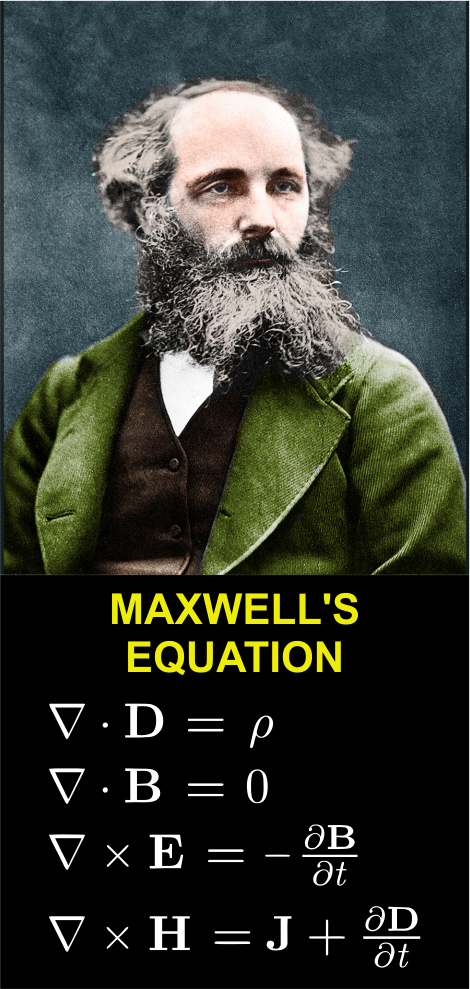 The Wave Equation
The Wave Equation
- Jean-Baptiste le Rond d’Alembert, a French polymath, developed an equation in 1743 that described the vibrations of an oscillating string or wave movement.
- The Equation is – 1/v^2 * ∂^2y/∂t^2= ∂^2y/∂x^2
- When extended to two or more dimensions, the wave equation allows researchers to predict the movement of water, seismic, and sound waves and serves as the foundation for quantum physics equations such as the Schrödinger equation, which underpins many modern computer-based gadgets.

Also Check Out: How to Learn Chemical Reactions Like A Pro
































