CBSE board is the central board that conducts board exams for classes 10th and 12th as these exams are conducted by central board authorities in the month of march and April. The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) is one of the most prestigious and oldest educational boards in India. CBSE Board syllabus is mainly based on NCERT textbooks, as they set question papers by taking reference to NCERT textbooks. And this is the reason each competitive exam follows NCERT for setting their question paper.
Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 Notes created by MTG’s experienced subject matter experts vividly explain the various aspects of naming and classification of the living world. You get to learn about the different habitats of the world such as cold mountains, deciduous forests, oceans, freshwater lakes, deserts, hot springs, etc from this study material. The Living World Class 11 Notes also tell you the differences between living and nonliving organisms. It is certainly one of the most reliable study aids that you can place your hands on for building the foundation of Class 11 biology.
Also Check out: Biological Classification Class 11 Notes Chapter 2
Importance of Biology Revision Notes
Biology Revision Notes for Class 11 CBSE – Quick revision notes for class 11 Biology are extremely useful for revising the entire syllabus during exam days. The revision notes cover all of the chapter’s important formulas and concepts. Even if you just want a quick overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to help. These notes will undoubtedly save you time on stressful exam days.
Biology is a fascinating subject, and the MTG Biology revision notes will help you prepare for your Class 11 CBSE exams. MTG’s expert-created Class 11 Biology NCERT notes cover the most recent CBSE curriculum, and these are well-researched CBSE notes that help students understand the topic clearly. Biology Notes for Class 11 are useful for a quick review because they are created by subject matter experts.
Must Check – Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 Important Question and Answer – The Living World
Topics Covered in The Living World Class 11 Notes
Notes prepared by MTG for biology chapter the living world covers topics like types of organisms present in our surrounding environment, their growth, types of nutrition they possess, types of metabolic activities they show.
The topics you will see in the notes are –
- Characters of living organism
- Taxonomy
- Fundamental components of taxonomy
- Differences between taxonomy and systematics
- Nomenclature
- Taxonomic aids
- Taxonomic keys
Biology Class 11 Chapter 1 The Living World Notes
Being alive is defined as a unique, complex organization of molecules expressing itself through chemical reactions which lead to growth, development, responsiveness, adaptation, and reproduction.
Characters of living organisms
Each organism has a specific structure that enables it to execute life-sustaining functions and activities like –
- Has definite organization.
- Has the ability of movement and locomotion.
- Shows metabolic functions, either catabolic (breaking down) or anabolic (building up).
- Shows adaptation to increase the survival rate.
- Reproduction for continuity of life.
- Respiration for the energy-generating process.
- Maintains homeostasis inside the body.
- Undergoes ageing after adulthood and then the natural death
The Living World Class 11 Notes pdf
Trending – 10 Important and Useful Mnemonics for Biology Students
TAXONOMY
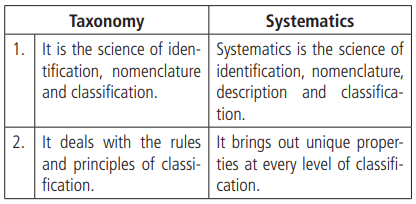
- Taxonomy (taxis – arrangement, nomos – law) is defined as the science dealing with the identification, nomenclature, and classification of organisms. It is the study of rules, principles and practice of classification, identification, and nomenclature of organisms.
- Taxonomy is also called systematic botany. Carolus Linnaeus is called the father of taxonomy or the father of systematic botany. H. Santapau is called the father of Indian taxonomy.
Fundamental components of the taxonomy
Classification – It is the placing of an organism or a group of organisms in a category according to a particular system and in conformity with a nomenclature system.
Identification – It is to determine the exact place or position of an organism in the set plan of classification.
Nomenclature – The process of giving scientific names to plants and animals is called nomenclature
Differences between taxonomy and systematics
You will also like: Top 10 Courses in Biology after Class 12 Except for MBBS
Nomenclature
- Nomenclature is the science of providing distinct and proper names to organisms as per the established universal practices and rules. Every taxonomists has to follow these rules.
- Binomial nomenclature is a system of classification introduced by Carolus Linnaeus, the 18th-century Swedish naturalist, in which each species is given two names.
- The first is the generic name, written with a capital letter, which designates the genus to which the species belong and the second is the specific name, indicating the species and then the name of the discoverer in full or in abbreviation. Example., Mangifera indica Linn.
- The scientific name is printed in italics. It is underlined in a handwritten description.
- The name of the author is kept in Roman script.
- The original names were taken from Latin and Greek languages. New names are now derived either from the Latin language or are Latinised. This is because the Latin language is dead and therefore, it will not change in form or spelling with the passage of time.
- There are five codes of nomenclature :
ICNB – International Code of Botanical Nomenclature.
ICZN – International Code of Zoological Nomenclature.
ICBacN – International Code of Bacteriological Nomenclature
ICVN – International Code of Viral Nomenclature
ICNCP – International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivation Plants
- The various categories used in classification can be arranged in a hierarchy, that is, ranked one above the other in descending order starting from the kingdom. The hierarchy indicates the various levels of kinship. The number of similar characters in categories decreases from lowest rank to highest rank. The hierarchical system of classification was introduced by Linnaeus.
- The hierarchy of major categories is Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class → Phylum or Division → Kingdom.
- Phylum – Phylum is a category higher than that of class. The term phylum is used for animals. A phylum is formed of one or more classes, e.g., the phylum Chordata of animals contains not only the class Mammalia but also aves (birds), reptilia (reptiles), amphibia (amphibians), etc. In plants, the term division is used in place of the phylum.
- Class – A class is made of one or more related orders. For example, the class dicotyledoneae of flowering plants contains all dicots which are grouped into several orders (e.g., rosales, sapindales, ranales, etc.) Likewise, class mammalia of animals includes all mammals which range from kangaroos (order marsupialia), rodents (order rodentia), carnivores (order carnivora) to great apes and man (order primata)
- Family – It is a taxonomic category that contains one or more related genera. All the genera of a family have some common features or correlated characters. They are separable from genera of a related family by important and characteristic differences in both vegetative and reproductive features. Thus the genera of cats (Felis) and leopard (Panthera) are included in the family felidae. The members of family felidae are quite distinct from those of family canidae (dogs, foxes, wolves). Similarly, the family solanaceae contains a number of genera like Solanum, Datura, Petunia and Nicotiana. They are distinguishable from the genera of the related family convolvulaceae (Convolvulus, Ipomoea)
- Order – The category includes one or more related families. Thus the plant family solanaceae is placed in the order polemoniales alongwith four other related families (convolvulaceae, boraginaceae, hydrophyllaceae and polemoniaceae). Similarly, the animal families felidae and canidae are included under the order carnivora along with hyaenidae (hyaenas) and ursidae (bears).
- Genus – It is a group or assemblage of related species which resemble one another in certain correlated characters. All the species of genus are presumed to have evolved from a common ancestor. A genus may have a single living species as Homo. Its species is Homo sapiens – the living or modern man. The genus Equus has many species, e.g., E. cabalus – the horse, E. vulgris – the ass, E. zebra – the zebra.
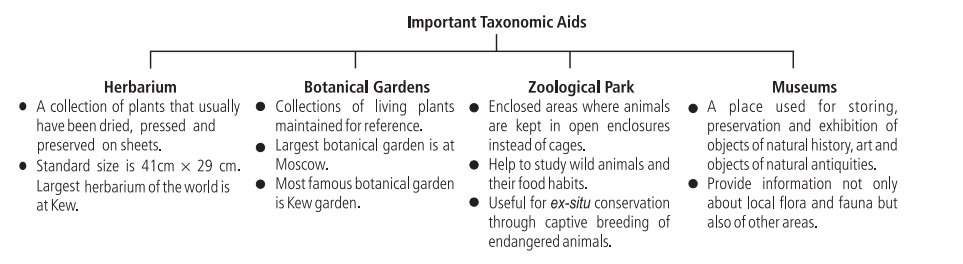
Taxonomic aids
- Techniques, procedures, and stored information that are useful in the identification and classification of organisms are called taxonomic aids.
- Taxonomic keys are aids for the rapid identification of unknown plants and animals based on their similarities and dissimilarities. Keys are primarily based on stable and reliable characters. The keys are helpful in a faster preliminary identification which can be backed up by confirmation through comparison with a detailed description of the taxon provisionally identified. Separate taxonomic keys are used for each taxonomic category like family, genus, and species.
Latest: 9 Amazing Biology Facts You Should Know