Many important questions are formed in competitive exams like CUET, JEE, NEET, and boards from Class 12 Physics Unit – 2. These questions are more likely to be asked in the exam; hence, students must practice them thoroughly. Below, we have provided Important Questions from Class 12 Physics Unit – 2 Current Electricity for your CUET 2023 preparation. You can check it here for revision purposes.
CUET Subjectwise Questions
Current Electricity Class 12 CUET Questions and Answers
We’ve compiled a list of important questions about the Current Electricity physics class 12 Unit – 2 that you should not miss while studying for your CUET Exams.
Current Electricity MCQ for CUET
Arrange the following materials in increasing order of their resistivity, Nichrome, Copper, Germanium, Silicon
Materials Resistivity (r)(W m at 0°C) Copper (Cu) 1.7 × 10–8 Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Fe, Cr) 100 × 10–8 Germanium 0.46 Silicon 2300 Hence, the option (a) is correct.
A current carrying wire in the shape of a circle as the current progresses along the wire, the direction of current density changes in an exact manner while the current I remains unaffected. The responsible factor for it is
The direction of current density is the direction of flow of positive charge in the circuit which is possible due to electric field produced by charges accumulated on the surface of wire.
Metre bridge is used to
A boy has two spare light bulbs in his drawer. One is marked 240 V and 100 W and the other is marked 240 V and 60 W. He tries to decide which of the following assertions are correct?
In the circuit, the power dissipated in the 10 W resistor is 40 W. Power dissipated in 12 W resistor is

For driving a current of 3 A for 5 minutes in an electric circuit, 900 J of work is to be done. Find the emf of the source in the circuit.
A carbon resistor of (47 ± 4.7) kW is to be marked with rings of different colours for its identification. The colour code sequence will be
In parallel combination of n cells, we obtain
In parallel combination of cells the voltage across the terminals is same and resistance is minimum. Therefore from V = IR, the current drawn from cell combination will be more
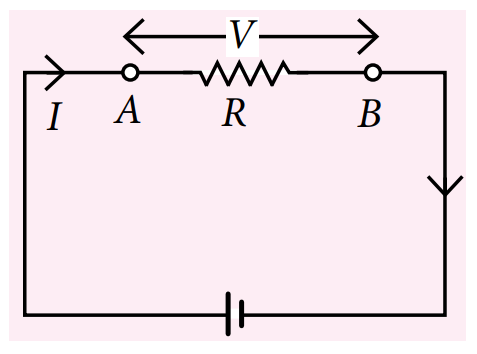
The reading of ammeter shown in figure is

A current of 2 A flows through a 2 W resistor when connected across a battery. The same battery supplies a current of 0.5 A when connected across a 9 W resistor. The internal resistance of the battery is
Current Electricity Assertion Reason Questions for CUET
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given and a corresponding statement of Reason (R) is given just below it. Of the statements, pick the correct answer as :
Assertion : The current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the drift velocity. Reason : As the drift velocity increases the current following through the conductor decreases.
Assertion : The average thermal velocity of the electrons in a conductor is zero. Reason : Direction of motion of electrons are randomly oriented.
In normal conductor, the direction of electrons are randomly oriented such that the total sum of their velocities is equal to zero.
Assertion : Fuse wire must have high resistance and low melting point. Reason : Fuse is used for small current flow only
Assertion : When n cells, each of internal resistance r are arbitrary connected in series , the total internal resistance of cells may be zero. Reason : The internal resistance depends on polarity of cell connected in circuit.
Looking to Step up your preparation for the upcoming CUET Exams? Check out
These CUET Prep Guides by MTG are your chance to score your best in CUET exam and get your dream college.
Buy Now – https://t.co/Sz1E8vlIp5#CUET #CUET2022 #CUETExam #cuetprepguide #mtgbooks #CUETApplication #NTA #UGcourses #entrance #cuetbooks #PracticePapers #Latestpattern pic.twitter.com/kkL9YDKcSR— MTG Books (@MTGBooks) June 13, 2022
Current Electricity CASE BASED MCQs for CUET
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
HEAT PRODUCED BY ELECTRIC CURRENT
Whenever an electric current is passed through a conductor, it becomes hot after some time. The phenomenon of the production of heat in a resistor by the flow of an electric current through it is called heating effect of current or Joule heating. Thus, the electrical energy supplied by the source of emf is converted into heat. In purely resistive circuit, the energy expended by the source entirely appears as heat. But if the circuit has an active element like a motor, then a part of the energy supplied by the source goes to do useful work and the rest appears as heat. Joule’s law of heating form the basis of various electrical appliances such as electric bulb, electric furnace, electric press etc.
Q. Which of the following is a correct statement?
(a) Heat produced in a conductor is independent of the current flowing.
(b) Heat produced in a conductor varies inversely as the current flowing.
(c) Heat produced in a conductor varies directly as the square of the current flowing.
(d) Heat produced in a conductor varies inversely as the square of the current flowing.
A. (c) : According to Joule’s law of heating,
Heat produced in a conductor, H = I 2Rt
where I = Current flowing through the conductor
R = Resistance of the conductor
t = Time for which current flows through the conductor.
so: H ∝ I2
Q. If the coil of a heater is cut to half, what would happen to heat produced ?
(a) Doubled (b) Halved (c) Remains same (d) Becomes four times
A. (a)
Q. A 25 W and 100 W are joined in series and connected to the mains. Which bulbs will glow brighter ?
(a) 100 W
(b) 25 W
(c) both bulbs will glow brighter
(d) none will glow brighter
A. (b)
Q. A rigid container with a thermally insulated wall contains a coil of resistance 100 W, carrying current 1 A. Change in its internal energy after 5 min will be
(a) 0 kJ (b) 10 kJ (c) 20 kJ (d) 30 kJ
A. (d): R = 100 Ω; I = 1 A ; t = 5 min. = 5 × 60 = 300 s
Change in internal energy = heat generated in coil = I 2 Rt = ((1)2× 100 × 300) J = 30000 J = 30 kJ
Q. The heat emitted by a bulb of 100 W in 1 min is
(a) 100 J (b) 1000 J (c) 600 J (d) 6000 J
A. (d): Here, P = 100 W, t = 1 min = 60 s
Heat developed in time t
H = P × t = (100 W)(60 s) = 6000 J
CUET 2022 Sample paper? check out – CUET Sample Paper 2022 PDF Download With Solutions
Hope you liked these questions, let us know if you need any explanations in the above questions. Want to Practice more?
Check out – CUET (UG) Common University Entrance Test-15 Practice Test Papers – Science Stream
Stay tuned for more questions and answers as we will update this page in the future.





























