In this chapter from Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal kingdom, you will get to practice various topics like Phylum Porifera, Phylum Coelenterata, Phylum Plathyhelminthes, Phylum Annelida, Phylum Arthropoda, etc. Below, we have provided Important Questions PDFs from Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom for your CBSE preparation. You can check it here or download it later for revision purposes.
Animal Kingdom Class 11 Important CBSE Questions and Answers
We’ve compiled a list of important questions about the Animal Kingdom biology class 11 chapter 4 that you should not miss while studying for your board exams.
Q.1. Study the given hierarchial chart and select the correct option for X and Y in terms of housefly classification.
Kingdom ← Phylum ← X ← Order ← Y ← Genus ← Species X Y
(a) Insecta Muscidae
(b) Musca Diptera
(c) Diptera Insecta
(d) Muscidae Arthropoda
A.1. (a): The hierarchial classification for housefly is as follows:
Kingdom – Animalia
Phylum – Arthropoda
Class – Insecta
Order – Diptera
Family – Muscidae
Genus – Musca
Species – domestica
Q.2. Birds and mammals share one of the following characteristics as a common feature.
(a) Pigmented skin (b) Pneumatic bones
(c) Viviparity (d) Warm blooded
A.2. (d): Both birds and mammals are homoiotherms (warm blooded) i.e., they have ability to maintain constant body temperature inspite of changes in ambient conditions.
Q.3. Which of the following animals is correctly matched with its particular taxonomic category?
(a) Dog – Familiaris, family
(b) Housefly – Musca, genus
(c) Wheat – Poales, class
(d) Mango – Dicotyledonae, Division
A.3. (b): The family of dog is Canidae while Familiaris is the genus. Poales is the order of wheat. Dicotyledonae is the class of mango.
Important CBSE Resources –
The Living World Class 11 Notes
The Living World CBSE Questions and Answers
Biological Classification Class 11 Notes
Biological Classification CBSE Questions and Answers
Plant Kingdom CBSE Questions and Answers
Q.4. Choose the correct scientific name of a frog.
(a) Ocimum sanctum (b) Canis familiaris
(c) Rana tigrina (d) Panthera pardus
A.4. (c)
Q.5. Give common names and phylum of :
(i) Gorgonia
(ii) Pennatula
A.5. (i) Gorgonia – Sea-fan
(ii) Pennatula – Sea-pen Both belong to Phylum Coelenterata
Here’s Proof for our 100% –
Buy yours now for Intensive Knowledge & 100% Learning in CBSE exams and attract topper-like scores now here – https://t.co/vD35gNqMHA#mtg #mtglearningmedia #mtgbooks #100percent #cbseboards #cbseexams #boardexams #boards #class10exams #class12exams #class10boards #class12boards pic.twitter.com/hiQnTqK94F
— MTG Books (@MTGBooks) December 2, 2022
Q.6. Assertion: All mammals are viviparous and have well developed placenta.
Reason: Mammals possess milk producing glands and nourish their young ones.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
A.6. (d): Few mammals are oviparous, e.g., platypus and spiny anteater.
Q.7. Read the following and answer questions
Phylum X of Kingdom Animalia is the largest phylum. Its members occur on land, in soil, in sea water, etc. The body consists of head, thorax and abdomen and have thick, tough covering which forms exoskeleton. They show sexual dimorphism and fertilisation is usually internal
(i) Identify the phylum X.
(a) Aschelminthes (b) Arthropoda
(c) Echinodermata (d) Mollusca
A. (b): Arthropoda is the largest phylum of Animal Kingdom.
(ii) What is the characteristic feature of phylum X?
(a) Soft bodied animals (b) Spiny skin
(c) Jointed appendages (d) Porous body
A. (c)
(iii) Select the odd one out, regarding ‘X’.
(a) Anopheles (b) Periplaneta
(c) Palaemon (d) Pheretima
A. (d): Pheretima (earthworm) is an annelid.
(iv) Which of the following is not true for members of phylum X?
(a) Malpighian tubules are excretory organs.
(b) Non-living chitinous cuticle forms an exoskeleton.
(c) Closed type blood vascular system.
(d) Statocyst as balancing organ.
A. (c): In arthropods, blood vascular system is of open type, i.e., blood does not flow in definite vessels
(v) Type of body cavity present in members of phylum X is
(a) haemocoel (b) schizocoel
(c) enterocoel (d) hydrocoel.
A. (a): In arthropods, the body cavity is hemocoel, i.e., cavityfilled with blood.
Need Assertion Reason Questions for Animal Kingdom ? Check Out –
Q.8. What are the general characteristics of Pleurobrachia?
A.8. General characters of Pleurobrachia, a ctenophore are:
(i) It is exclusively marine.
(ii) It shows bioluminescence.
(iii) It has biradial symmetry.
(iv) It is diploblastic and have tissue level of organisation.
(v) It shows locomotion with comb plates.
Q.9. Complete the following table of organisms with their taxonomic categories.
| Common Name | Biological Name | Class | Phylum/ Division |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Homo sapiens | Mammalia | Chordata |
| Mango | B | C | Angiospermae |
| Wheat | Triticum aestivum | Monocotyledonae | D |
A.9. A – Man
B – Mangifera indica
C – Dicotyledonae
D – Angiospermae
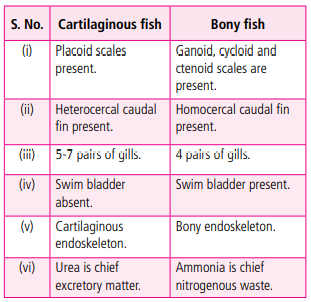
Q.10. Differentiate between cartilaginous and bony fishes
Q.11. Why are cnidarians called so?
A.11. The name cnidaria is derived from cnidoblasts or cnidocysts (which contain the stinging capsules or nematocysts) present on the tentacles and body. Cnidoblasts are used for anchorage, defense, and capture of prey.
Q.12. Give any 3 general characters of Wuchereria
A.12. General characters of Wuchereria, an aschelminth are :
(i) It has organ system level of organisation.
(ii) It is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and pseudocoelomate animal.
(iii) It shows internal fertilisation.
Q.13. What is polymorphism?
A.13. Polymorphism is the occurrence of several different types of individuals in a single species during life cycle or as member of colony. It is commonly seen in Class Hydrozoa of Phylum Cnidaria. Three main types of individuals are-polyp, blastostyles and medusa. Polyp are generally sessile, cylindrical body, asexual zooid
which are mainly nutritive in function. Blastostyles give rise to reproductive individuals, the medusae by budding. Medusa is free swimming, umbrella shaped with marginal tentacles and centrally located mouth, sexual zooid.
Q.14. What are nematocysts?
A.14. Nematocysts are not cells but cell organelles. It is contained within the cnidoblast and develops from interstitial cells of epidermis and migrate via mesogloea to tentacles (most abundant on tentacles). Cnidocil, the most sensitive part of nematocyst, is present on the external surface of cnidoblast and can be triggered by mechanical or chemical stimuli. The nematocyst consists of a large oval capsule called butt and a fine thread tube. The capsule is filled with a poisonous toxic fluid called hypnotoxin (= a mixture of phenol and protein). The thread tube consists of three parts – shaft (a short wide funnel shaped), spinneret bearing three large pointed barbs or styles and six spiral ridges bearing spines and a long narrow filament coiled around the shaft. Nematocyst are connected to a contractile bundle of myonemes known as lasso, which prevent their detachment. Nematocysts serve for offence, defence, locomotion, food capture and anchorage
Q.15. Discuss the general characters of the Class Aves.
A.15. General characters of Class Aves are :
(i) Birds are bipedal, feathered and warm blooded animals.
(ii) Forelimbs are modified into wings.
(iii) Hindlimbs are adapted for perching, walking or swimming, etc.
(iv) Upper and lower jaws are modified into beak, teeth are absent.
(v) Heart is four chambered.
(vi) Endoskeleton is fully ossified and bones are pneumatic, filled with air instead of bone marrow.
(vii) Body is spindle shaped to offer minimum resistance to the wind.
(viii) Air sacs are attached to the lungs, which serve as reservoirs of air.
Examples : Psittacula (Parrot), Columba (Pigeon), Neophron (Vulture), Tyto (Owl), Pavo (Peacock).
Are you Practicing enough?