In this chapter from Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 plant kingdom, you will get to practice various topics like the Phylogenetic System of classification, Numerical Taxonomy, Cytotaxonomy, Chemotaxonomy, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms, etc. Below, we have provided Important Questions PDFs from Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom for your CBSE preparation. You can check it here or download it later for revision purposes.
Recent – Plant Kingdom NEET Questions and Answers
Plant Kingdom Class 11 Important Questions and Answers
Q.1. All are plant characteristics except
I. Cellular cell wall II. Absence of musculature III. Absence of response to stimuli IV. Ability to manufacture food.
(a) I and II (b) III and IV
(c) III only (d) IV only
A.1. (c): All living organisms respond to stimuli. Plants also do so although their response may be slow like growth of roots towards gravity and growth of shoot towards sunlight.
Q.2. The plant body is thalloid in
(a) Marchantia (b) Salvinia
(c) Funaria (d) Sphagnum.
A.2. (a)
Q.3. Define protonema stage.
A.3. A juvenile autotrophic filamentous stage of mosses is called protonema.
Q.4.Assertion: In pteridophytes sporophytic phase is longer lived while gametophytic phase is shorter lived.
Reason: Both sporophyte and gametophyte are independent in pteridophytes.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
A.4. (b)
Important CBSE Resources –
The Living World Class 11 Notes
The Living World CBSE Questions and Answers
Biological Classification Class 11 Notes
Biological Classification CBSE Questions and Answers
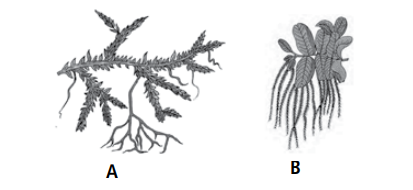
Q.5. Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to (v).
Riya and her friends along with their teachers went to Mussorrie on educational tour where they collected different types of pteridophytes. They are seedless vascular plants that generally occur in cool, damp and shady places. They observed the collected samples carefully.
(i) Identify the plants A and B shown in figure and select the correct option.
| A | B |
|---|---|
| (a) Equisetum | Fern |
| (b) Selaginella | Equisetum |
| (c) Selaginella | Salvinia |
| (d) Equisetum | Fern |
A. (c)
(ii) In A, main plant body is a (i) , which is (ii) into true roots, stem and leaves.
| (i) | (ii) |
|---|---|
| (a) sporophyte | differentiated |
| (b) sporophyte | not differentiated |
| (c) gametophyte | not differentiated |
| (d) gametophyte | not differentiated |
A. (a)
(iii) In B, a spore germinates to produce
(a) sporophyte (b) sporogonium
(c) prothallus (d) microsporophyll.
A. (c): In pteridophytes, spore is a haploid structure, which develops after meiosis of spore mother cell. On germination, it gives rise to a green haploid prothallus (gametophyte) which is monoecious, i.e., has both antheridia (male sex organs) and archegonia (female sex organs).
(iv) The prothallus of both (A) and (B) produces
(a) sporangia
(b) antheridia and archegonia
(c) vascular tissues
(d) root, stem and leaf
A. (b)
(v) Select the correct statement for plant A and B.
(a) Both A and B are heterosporous.
(b) A is homosporous whereas B is heterosporous.
(c) Both A and B are homosporous.
(d) A is heterosporous whereas B is homosporous.
A. (a): Both plants A and B, Selaginella and Salvinia respectively are heterosporous i.e., produce two types of spores, microspores and megaspores.
Your Question Bank for Your CBSE Journey –
10 Years CBSE Champion Chapterwise-Topicwise
Q.6. Write a brief note on Kingdom Plantae
A.6. Kingdom Plantae includes all eukaryotic chlorophyll containing organisms – Algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms. The plant cells have eukaryotic structure with prominent chloroplasts and cells are mainly made up of cellulose. The mode of nutrition is autotrophic but few members are partially heterotrophic such as insectivorous plants or parasites. The common examples of insectivorous plants are bladderwort and Venus flytrap, whereas common example of parasite is Cuscuta. They show distinct alternation of generation.
Q.7. Brinjal and potato belong to the same genus Solanum, but to two different species. What defines them as separate species?
A.7. Brinjal and potato belong to same genus Solanum but they are different species Solanum melongena and Solanum tuberosum respectively. The basic criterion for defining two different species is that they cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Potato and brinjal neither actually nor potentially interbreed, thus they are defined as separate species.
Q.8. Differentiate between isogamy and anisogamy.
A.8. Differences between isogamy and anisogamy are as follows:
| S.No. | Isogamy | Anisogamy |
|---|---|---|
| (i) | The fusing gametes are similar in structure, size and behaviour. | There is equal storage of food in the fusing gametes |
| (ii) | There is no distinction of male and female gametes. | A distinction of male and female gametes is present. |
| (iii) | There is equal storage of food in the fusing gametes | More food is stored in female gametes. |
Q.9. Refer to the given figures and answer the following questions.
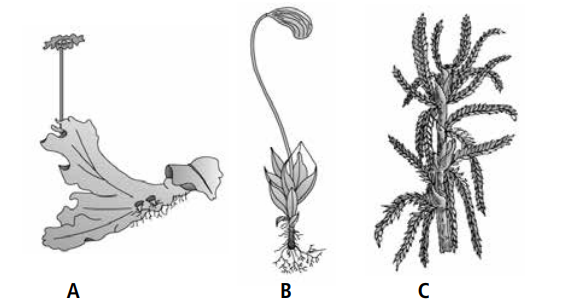
(i) Identify the figures A, B and C.
A. A – Male thallus of Marchantia B – Funaria C – Sphagnum
(ii) To which group these three belong?
A. Marchantia is a liverwort while Funaria and Sphagnum are mosses. These three belongs to division Bryophyta.
(iii) Which among these three are used in trans-shipment of living materials? Why?
A. Sphagnum (C) is used as packing material for trans-shipment of living materials because of its capacity to hold water.
Q.10. What are the differences between liverworts and mosses?
A.10. Differences between liverworts and mosses are as follows:
| S. No. | Liverworts | Mosses |
|---|---|---|
| (i) | Branching is generally dichotomous. | Branching is lateral and extra-axillary. |
| (ii) | Seta develops rapidly towards the maturity of spores. | Seta grows slowly over a long period and fully developed before the spores mature. |
| (iii) | Capsule often possesses elaters. | Elaters are absent. |
| (iv) | Peristome teeth are absent | Peristome teeth occur towards the apical region of the capsule |
| (v) | Columella is generally absent | Capsule contains a sterile columella |
Q.11. Explain how gametophyte is a dominant phase in the life cycle of a bryophyte.
A.11. Bryophytes are a group of the simplest and primitive plants belonging to embryophyta. Gametophytic and sporophytic phases are present in the life cycle of bryophytes and both these phases are morphologically distinct (heteromorphic). Gametophytic phase in bryophytes is more conspicuous, long lived, independent, green and freely branched whereas, the sporophytic phase is short lived and dependent upon the gametophyte. The main plant body of the bryophyte is haploid and bears sex organs, i.e., antheridium and archegonium. Antheridium produces a number of flagellate male gametes called sperms or antherozoids and archegonium is flask shaped with tubular neck and swollen center. The gametophytic plant body of bryophytes is thalloid in liverworts whereas foliose in mosses. In liverworts, the thallus is differentiated into a dorsal photosynthetic and ventral storage region. Sex organs antheridia and archegonia are either distributed on the dorsal surface of the thallus or are on distinct receptacles. In mosses, the gametophyte has two growth stages
(i) Protonema stage- It is the juvenile stage represented by prostrate, creeping, green and branched filamentous structure; it develops from the spore and is only a transitory vegetative stage and
(ii) leafy stage or gametophore – an erect cylindrical shoot with persistent leaves and sex organs.
Q.12. Give a brief account on
(a) sporophyte of pteridophyte
A. Sporophyte of pteridophyte : The plant body is generally herbaceous and is differentiated into true roots, stems and leaves. Roots are of adventitious type. Branching of stem is of dichotomous type in some while monopodial in others. Leaves are either microphyllous (small) e.g., Selaginella or megaphyllous (large) e.g. ferns (large leaves of ferns are called fronds). The sporophyte reproduces asexually by means of spores which develops inside the sporangia, subtended by sporophylls. The sporangia bearing leaves or leaf-like appendages are called sporophylls. In some cases e.g., Selaginella and Equisetum, sporophylls may form distinct compact structures called strobili or cones. The sporangia produce haploid spores by meiosis in diploid spore mother cells (sporocyte). The spores on germination give rise to the haploid gametophyte or prothallus which are usually small or insignificant structure.
(b) gametophyte of pteridophyte.
A. Gametophyte of pteridophyte: Gametophyte is inconspicuous, small, multicellular, mostly photosynthetic thalloid structure that bears the sex-organs, the antheridia (male organ) and archegonia (female organ).
The thalloid gametophyte or prothallus requires cool, damp, shady places to grow. The megaspores and microspores germinate and give rise to female and male gametophytes respectively. The female gametophytes in these plants are retained on the parent sporophytes for viable periods. In heterosporous ferns, the female gametophyte depends on food stored by the megaspore.
Aim for 100% Learning with –